In a collaboration project with UCL, Dina Ibrahim (UCL) has developed a supercapacitor integrated into a printed circuit board. Read the full article here.
Abstract
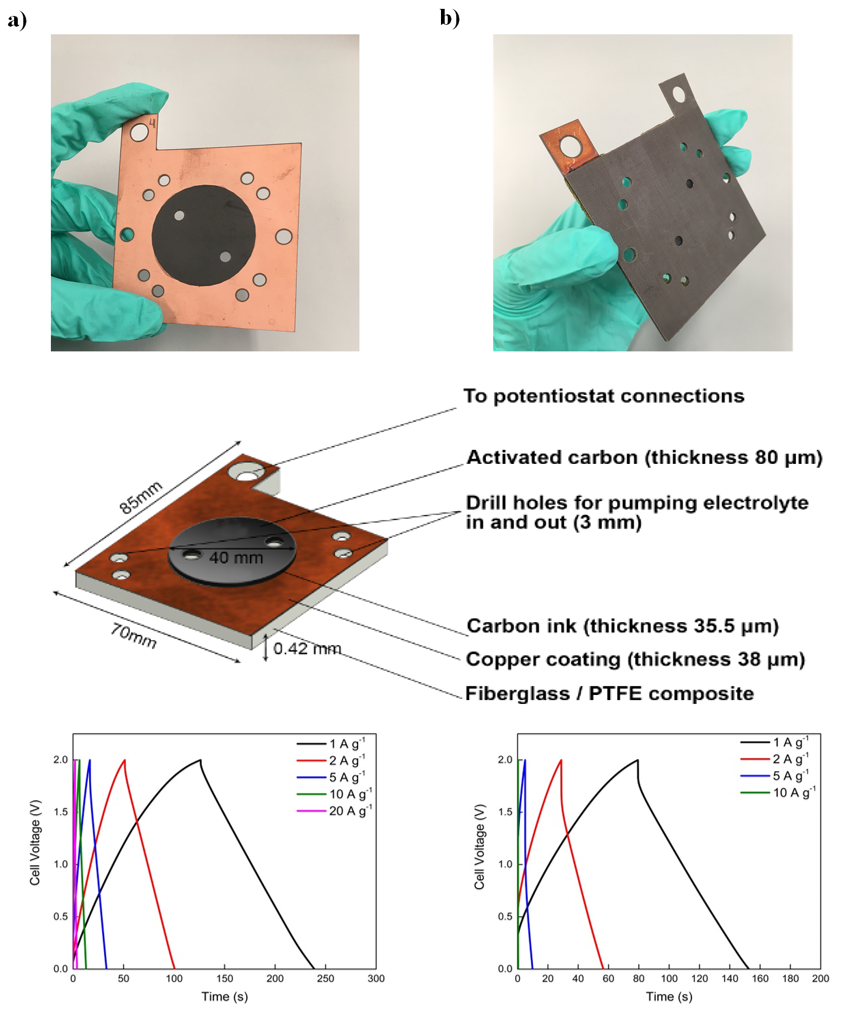
Physically integrated energy storage devices are gaining increasing interest due to the rapid development of flexible, wearable and portable electronics technology. For the first time, supercapacitor components have been integrated into a printed circuit board (PCB) construct. This proof-of-concept study paves the way for integrating supercapacitors into power electronics devices and hybridising with PCB fuel cells. Commercial Norit activated carbon (NAC) was used as the electrode material and was tested in two types of electrolytes, sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) aqueous electrolyte, and Na2SO4-polyvinyl alcohol (Na2SO4-PVA) gel electrolyte. Electrochemical measurements compare the SC-PCBs to standard two-electrode button-cell supercapacitors. A volumetric energy density of 0.56 mW h cm−3 at a power density of 26 mW cm−3 was obtained in the solid-state SC-PCB system, which is over twice the values acquired in the standard cell configuration. This is due to the removal of bulky components in the standard cell, and/or decreased thickness of the overall device, and thus a decrease in the total volume of the SC-PCB configuration. The results show great potential for embedding supercapacitors into PCBs for a broad range of applications. In addition, further advantages can be realised through close physical integration with other PCB-based electrochemical power systems such as fuel cells.